Are you tired of projects exceeding budget and failing to meet their goals? Managing project cost is crucial for success, yet it can be daunting for even the most experienced project managers.
Identifying and calculating project expenses can be complex, from direct and indirect costs to fixed and variable expenses. However, with the right strategies and tools, you can gain control over your project’s finances and maximize your resources for success.
In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of project budget management and provide essential tips and tricks for managing your project expenditure effectively. So let’s dive in!
Throughout this article, we’ll discuss:
- Identifying Project Costs
- Calculating Project Expenses
- Tips for Managing Project Expenditure
- Common Challenges in Project Budget Management
- Best Cost Control and Project Financial Management Tools
- Wrap-up: Improve Your Project Pricing Management with Ongoing Cost Control

How to Identify Project Expenses?
We can categorize project budgets into several categories. Understanding how to differentiate between various project expenses is essential for budgeting and cost management.
Direct Vs. Indirect Costs
Project expenses can be broadly classified into two categories: direct costs and indirect costs. Direct costs are expenses directly attributed to a specific project activity or task. These costs are generally easy to identify and quantify. Examples of direct costs include:
- Labor costs: Wages, salaries, benefits, and bonuses for project team members.
- Materials costs: The cost of raw materials, supplies, and equipment needed to complete a project.
- Equipment costs: The cost of renting or purchasing equipment, such as machinery or vehicles, needed for the project.
- Subcontractor costs: Payments made to subcontractors for their services.
- Travel costs: Transportation, lodging, and other expenses related to project-related travel.
- Software costs: The cost of purchasing or licensing software necessary for the project.
On the other hand, indirect costs, also known as overhead costs, are expenses that cannot be directly attributed to a specific project task or activity. These costs are often shared among several projects or business units. Examples of indirect costs include
- Rent and utilities: Renting office space and utilities such as electricity, water, and internet.
- Insurance: The cost of insuring the project and its employees.
- Administrative costs: Support staff salaries and expenses such as administrative assistants, HR, and accounting teams.
- Marketing and advertising costs: Promoting the project to potential customers or clients.
- Legal costs: The cost of legal services needed for the project, such as drafting contracts or obtaining permits.
Fixed Vs. Variable Costs
When calculating project expense estimates, it’s essential to understand the difference between fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs are expenses that remain the same regardless of the project’s size or duration. Variable costs, on the other hand, are expenses that vary with the project’s size or duration.
Fixed costs are expenses that do not change with the production level or the amount of work done on a project. Examples of fixed costs include:
- Rent: Leasing an office space for the project’s duration.
- Salaries: The cost of paying full-time project team members for the entire project duration.
- Insurance: The cost of insuring the project and employees working on it for the entire project duration.
In contrast, variable costs are expenses that change with the production level or the amount of work done on a project. Examples of variable costs include
- Materials: The cost of raw materials needed for the project. The more materials are needed, the higher the variable cost.
- Labor: The cost of paying project team members per hour or task. The more work done, the higher the variable cost.
- Equipment: The cost of renting or buying the equipment needed for the project. The longer the equipment is used, the higher the variable cost.
Fixed costs are generally easier to budget for, as they do not change, whereas variable costs require more precise forecasting to ensure the project stays within budget.
Understanding fixed, and variable costs can help project managers make informed decisions regarding allocating resources and managing expenses. By identifying fixed and variable costs early on, project managers can develop a more accurate project budget and ensure that they have enough funds to complete the project successfully.
Tangible Vs. Intangible Costs
Finally, it’s also important to consider and understand both tangible and intangible costs. Tangible costs are expenses that can be easily quantified and measured in monetary terms. Examples of tangible costs include:
- Labor costs
- Materials costs
- Equipment costs
- Travel costs
- Software costs

Intangible costs, on the other hand, are expenses that are not easily quantifiable and cannot be measured in monetary terms. Examples of intangible costs include:
- Reputation
- Quality
- Morale
While intangible costs may not have a direct impact on the project’s budget, they can have a significant impact on the project’s success. For example, if the project takes longer than expected to complete, it can impact the team’s morale and job satisfaction, which can ultimately impact the project’s quality.
By considering all categorizations of project pricing, project managers can develop a more comprehensive view of the project’s expenses and ensure that they are taking all factors into account when making decisions.
How to Calculate Project Expenses?
Calculating project expenditure involves determining the total expenses associated with the project. Here are the steps to calculate project expenses:
Estimating Costs
Estimating costs involves determining the expected cost of each item identified in the project plan. Project managers can estimate costs by using historical data, market research, and expert opinions. It’s important to consider both direct and indirect costs when estimating project prices.
Creating a Budget
Once the costs have been estimated, project managers can create a budget that includes all costs associated with the project. The budget should include both direct and indirect costs and should be reviewed and approved by stakeholders before the project begins.
Tracking and Controlling Costs
Tracking and controlling costs involves monitoring project expenses and making adjustments to ensure that the project stays within budget. Project managers should regularly review the budget and compare actual expenses to the estimated costs. If the project is going over budget, project managers can make adjustments, such as reducing costs or reallocating resources, to bring the project back on track.
Tips for Managing Project Expenses
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing project budgets, you can utilize some key strategies to ensure your projects stay on budget.
1. Develop A Detailed Project Plan
Developing a detailed project plan can help project managers identify all costs associated with the project and create a comprehensive budget. The plan should include all project deliverables, timelines, and resources required to complete the project.

2. Prioritize Requirements
Project managers should work with stakeholders to prioritize project requirements based on their importance and impact on the project’s success. This can help project managers make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and budgeting.
3. Use Project Management Software
Project management software can help project managers track project expenses, monitor progress, and adjust the budget as needed. This can help project managers stay on top of costs and ensure that the project stays within budget.
4. Communicate with Stakeholders
Effective communication with stakeholders is critical to managing project pricing. Project managers should keep stakeholders informed of project expenses and progress, and work with them to make decisions when it comes to budgeting and resource allocation.
5. Monitor Project Expenses Regularly
Project managers should regularly monitor project expenses and compare actual costs to the budget. This can help project managers identify potential cost overruns and make adjustments to the budget as needed.
6. Be Proactive In Managing Risks
Risks can have a significant impact on project prices. Project managers should proactively identify and manage risks throughout the project lifecycle to minimize their impact on project expenditure.
7. Evaluate and Learn from Past Projects
Project managers should evaluate and learn from past projects to identify areas where costs can be reduced or eliminated. This can help project managers improve cost management practices and ensure that future projects are completed within budget.
Common Challenges in Project Budget Management
Having an idea about the various costs associated with a project and knowing how to calculate them is essential for effective cost management. However, there are several common challenges that project managers must face when it comes to managing project prices. These include:
1. Scope Creep
Scope creep occurs when the scope of the project expands beyond the original plan, which can lead to additional costs. Project managers should work with stakeholders to clearly define the project scope and establish change management processes to manage scope creep.
2. Resource Allocation
Resource allocation can be a challenge in project price management. Project managers should carefully allocate resources to ensure that the project stays within budget. This may involve balancing resource allocation across multiple projects or reallocating resources as needed to ensure project success.
3. Unexpected Costs
Unexpected costs can arise during the project lifecycle, such as unforeseen delays or additional expenses. Project managers should establish contingency plans to address unexpected costs and regularly monitor expenses to ensure that the project stays within budget.

4. Inaccurate Project Pricing Estimates
Sometimes, project managers underestimate or overestimate the cost of a project. This can lead to budget overruns or missed deadlines. To avoid inaccurate cost estimates, project managers should use tools such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and activity-based costing (ABC). These tools can help project managers better understand the costs associated with a project and make more accurate estimates.
5. Lack of Communication
Project expenditure management requires effective communication between stakeholders. Without proper communication, it can be difficult for project managers to identify and manage potential risks or challenges. Project managers should ensure that stakeholders know the budget and any changes that may occur during the project’s lifecycle.
Best Cost Control and Project Financial Management Tools
You’ll need the right tools and technologies to manage your project budget effectively. Here are some of the best cost control and project financial management tools available:
1. Day.io – Best Overall Project Expense Management and Time Tracking Tool
Day.io is an easy-to-use project pricing management and time-tracking tool designed to help you keep track of all your project expenses. With Day.io, you can create detailed budget estimates for each task or activity in your project and monitor actual costs against those estimates. You can also use the visual timeline to quickly identify any potential overruns or delays during your project schedule.
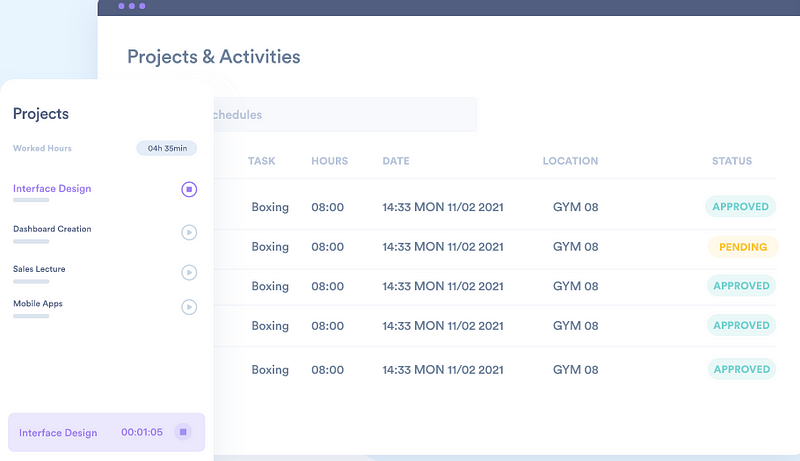
Features
- Project budget and billing estimation
- Time tracking with integrated cost calculation
- Project timeline visualization
- Real-time cost tracking and reporting
- Integrations with popular business tools
- Automated employee scheduling and planning
- Detailed timesheet reports with manual and automated approval
- Analytics and project reports
Pricing
Project and time tracking starts from $6 per user/month
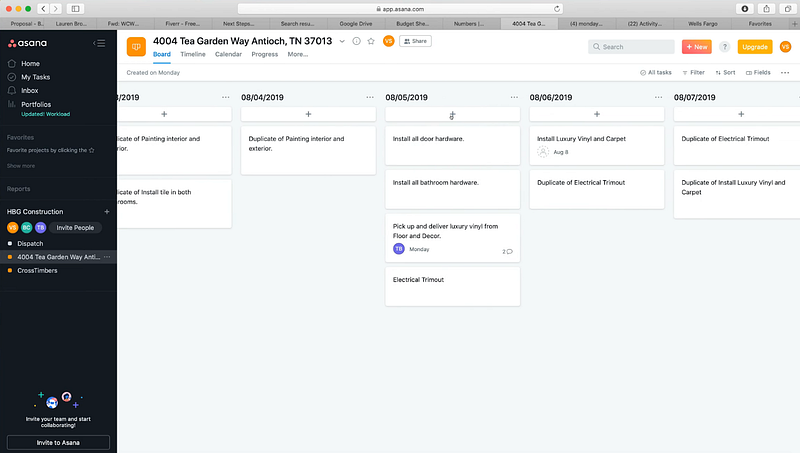
2. Asana – Excellent for Creating Project Pricing Estimates and Budget
Asana offers a reliable and user-friendly project management platform for creating cost estimates and budgeting. You can quickly get an overview of your project’s financial status by viewing the costs associated with each task or activity and tracking expenses over time. Asana also makes it easy to adjust budgets during a project if needed and helps improve your team’s productivity.
Features
- Task-based cost estimates
- Real-time budget tracking and reporting
- Integrations with popular business tools
- Collaboration, task management, and project timeline features
- Resource planning and optimization tools
Pricing
Premium plan starts from $10.99 per user/month.
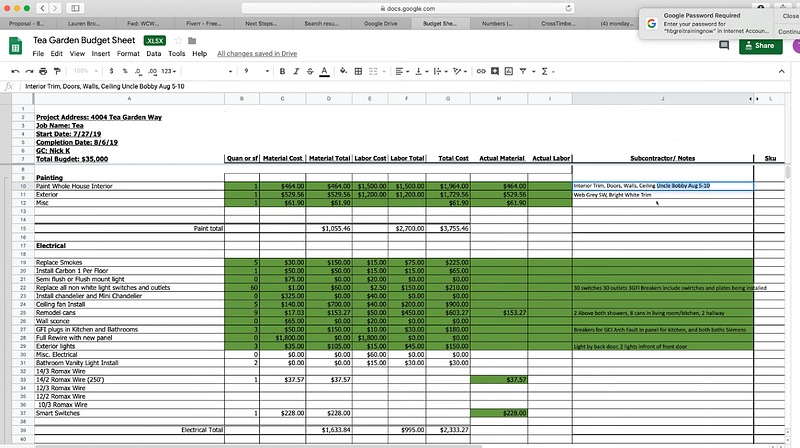
3. Microsoft Excel – Ideal for Basic Cost Management Calculations
Microsoft Excel is an excellent tool for basic cost management calculations. You can use Excel to keep track of project expenditures, create budget reports, and analyze data related to project expenditures. Plus, with its built-in formulas and functions, you can easily calculate the costs associated with different activities or tasks in your project.
Features
- Built-in formulas and functions
- Flexible data analysis tools
- Customizable reporting and budgeting templates
- Integrations with popular business tools
Pricing
Comes with Office 365, which costs $9.99 per month for a family of up to 6 users.

Wrap-up: Improve Your Project Budget Management with Ongoing Cost Control
Managing project prices can be difficult, but with the right strategies and tools, you can ensure that your projects stay within budget and meet their goals. Identifying and understanding project expenditure is essential for effective cost management.
Utilizing a project expense management and time tracking tool like Day.io allows you to keep track of project expenses in real-time, monitor expenses and revenue, and provide accurate forecasts for future projects. Sign up for Day.io today and explore its powerful features to evaluate costs of a project.